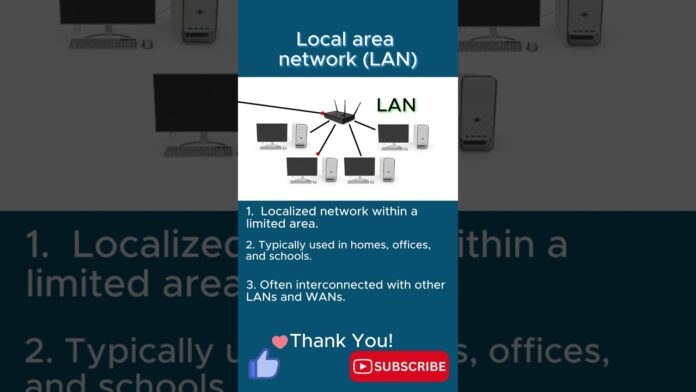
In the realm of network infrastructure, the Local Area Network (LAN) stands as the cornerstone of in-house connectivity, facilitating seamless communication and resource sharing among devices within a confined geographical area. From small businesses to large enterprises, LANs play a pivotal role in enabling collaboration, productivity, and innovation. In this article, we embark on a journey through the world of LANs, exploring their key features, benefits, and applications in modern networking.
Unveiling the Local Area Network (LAN):
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network infrastructure that connects devices within a limited geographical area, such as an office building, campus, or residential home. LANs are characterized by their relatively small scale, high data transfer rates, and low latency, making them ideal for supporting local communication and resource sharing among connected devices.
Key Components of a LAN:
- Devices: A LAN typically consists of various end devices, including computers, printers, servers, IP phones, and IoT devices, all interconnected to facilitate data exchange and collaboration.
- Intermediary Devices: Intermediary devices such as switches, routers, and access points serve as the backbone of LAN infrastructure, enabling data transmission, network management, and connectivity to external networks.
- Cabling or Wireless Infrastructure: LANs can be wired or wireless, depending on the connectivity requirements and environmental constraints. Ethernet cables, fiber optic cables, and wireless access points are common components of LAN infrastructure.
Benefits of LANs:
- Resource Sharing: LANs allow users to share resources such as files, printers, and internet connections, enhancing collaboration and productivity within organizations.
- Centralized Management: With centralized management tools and protocols, LAN administrators can efficiently monitor, configure, and troubleshoot network devices and services.
- Cost-Effectiveness: LANs offer a cost-effective solution for in-house communication and connectivity, eliminating the need for expensive external network services.
- High Performance: LANs deliver high data transfer rates and low latency, ensuring fast and responsive communication for applications such as video conferencing, VoIP, and real-time data exchange.
Applications of LANs:
- Office Networking: LANs form the backbone of office networks, providing connectivity for computers, printers, and other essential devices, enabling seamless communication and collaboration among employees.
- Educational Institutions: LANs are widely used in schools, colleges, and universities to connect computers, classrooms, and administrative offices, facilitating e-learning, research, and academic collaboration.
- Home Networking: In residential settings, LANs enable connectivity for smart home devices, entertainment systems, and personal computers, enhancing convenience and entertainment options for homeowners.
The Local Area Network (LAN) is a fundamental building block of modern network infrastructure, enabling efficient communication, resource sharing, and connectivity within confined geographical areas. From office networks to educational institutions and residential homes, LANs play a vital role in fostering collaboration, productivity, and innovation. As we embrace the digital age and the era of interconnectedness, LANs will continue to evolve, adapting to the changing needs and demands of users and organizations alike, driving the next wave of connectivity and innovation in networking.