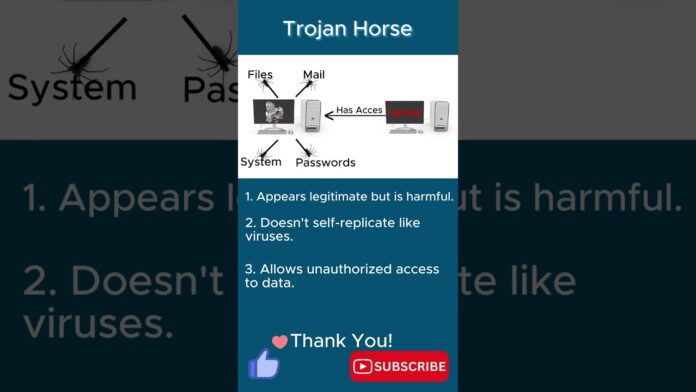
In the realm of cybersecurity, Trojan horses represent a formidable and deceptive threat to network integrity and data security. Named after the legendary Greek tale of the wooden horse used to infiltrate the city of Troy, these malicious programs masquerade as legitimate software to deceive users and gain unauthorized access to systems. In this article, we explore the insidious nature of Trojan horse threats, shedding light on their tactics, detection methods, and strategies for prevention.
Understanding Trojan Horses:
A Trojan horse is a type of malware that disguises itself as legitimate software or files to trick users into installing or executing them. Unlike viruses or worms, which propagate and spread independently, Trojan horses rely on social engineering tactics to infiltrate systems. Once installed, Trojan horses can perform a variety of malicious activities, including:
- Backdoor Access: Creating a hidden backdoor or remote access point that allows attackers to gain unauthorized access to compromised systems.
- Data Theft: Stealing sensitive information, such as login credentials, financial data, and personal files, for identity theft or financial fraud purposes.
- Spying and Surveillance: Monitoring user activities, capturing keystrokes, recording screen sessions, and eavesdropping on communications to gather intelligence or conduct espionage.
- Botnet Recruitment: Enlisting infected systems into botnets, distributed networks of compromised devices controlled by malicious actors for coordinated cyber attacks or spam campaigns.
Modes of Trojan Horse Transmission:
Trojan horses can be distributed through various vectors, including:
- Email Attachments: Concealing Trojan payloads within email attachments or links leading to malicious websites, exploiting human curiosity or urgency to trick users into opening them.
- Software Downloads: Bundling Trojan-infected software or files with legitimate applications, freeware, or pirated content distributed through file-sharing networks or malicious websites.
- Drive-by Downloads: Exploiting vulnerabilities in web browsers, plugins, or software applications to silently download and install Trojan payloads when users visit compromised or malicious websites.
- Social Engineering: Leveraging social engineering tactics, such as phishing emails, fake software updates, or deceptive advertisements, to lure unsuspecting users into downloading and executing Trojan-laden files.
Detecting and Mitigating Trojan Horses:
Detecting and mitigating Trojan horse threats requires a multi-layered approach to network security, including:
- Antivirus and Anti-Malware Solutions: Deploying robust antivirus and anti-malware software capable of detecting and removing Trojan infections from compromised systems.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Implementing firewalls and IDS solutions to monitor network traffic, detect suspicious behavior indicative of Trojan activity, and block malicious connections.
- Behavioral Analysis: Employing behavioral analysis techniques to identify anomalous system behavior, such as unauthorized access attempts, data exfiltration, or unusual network traffic patterns associated with Trojan activity.
- User Education and Awareness: Educating users about the risks of Trojan horse threats, phishing scams, and unsafe browsing habits to reduce the likelihood of inadvertently downloading or executing Trojan-laden files.
Prevention Strategies:
To prevent Trojan horse infections and safeguard network integrity, organizations should implement the following preventive measures:
- Software Updates: Keeping operating systems, applications, and security software up-to-date with the latest patches and security updates to mitigate known vulnerabilities exploited by Trojan horses.
- Download Vigilance: Exercising caution when downloading and installing software from untrusted sources, verifying the authenticity and integrity of software downloads to avoid inadvertently installing Trojan-infected programs.
- Access Control: Implementing least privilege principles and role-based access controls (RBAC) to restrict user permissions and limit access to sensitive data and resources, reducing the risk of Trojan infiltration and data compromise.
- Network Segmentation: Segmenting network infrastructure into separate zones or VLANs to contain Trojan infections and prevent lateral movement within the network, limiting the scope of potential damage and data exfiltration.
Trojan horse threats pose a significant risk to network security and data privacy, leveraging deception and stealth to infiltrate systems, steal sensitive information, and compromise organizational integrity. By understanding the tactics and behaviors of Trojan horses, implementing proactive detection and mitigation measures, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness and vigilance, organizations can effectively mitigate the risks posed by Trojan horse threats and safeguard their networks from clandestine intrusions and data breaches. In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, resilience, innovation, and collaboration are paramount in the ongoing battle against Trojan horse threats and other emerging cyber threats, ensuring the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of network resources and data assets.