In the vast landscape of network topologies, simplicity and effectiveness often reign supreme. Among the array of options available, the bus network topology stands out for its straightforward design and practical applications.
Understanding the Bus Network Topology:
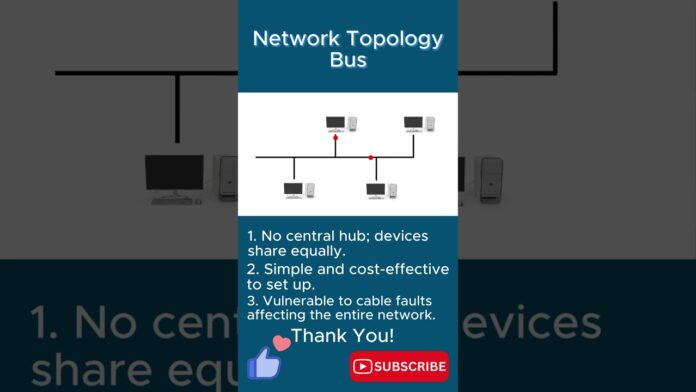
The bus network topology is characterized by a single communication channel, often referred to as a “bus,” to which all devices are connected. Devices share this common communication medium, with data transmitted along the bus from one end to the other. Each device receives the transmitted data but only processes information intended for it, based on unique identifiers or addresses.
Advantages of Bus Topology:
- Simplicity: The bus topology is inherently simple, featuring a linear arrangement where devices connect directly to the main communication channel. This straightforward structure simplifies network setup and maintenance, making it an attractive option for small to medium-sized networks.
- Cost-Effectiveness: With its minimal hardware requirements, the bus topology offers a cost-effective solution for network connectivity. The absence of complex networking equipment, such as switches or routers, reduces infrastructure costs, making it an economical choice for budget-conscious organizations.
- Scalability: Bus networks are highly scalable, allowing for the addition of new devices without significant disruption to existing infrastructure. Devices can be easily connected to the bus using standard network interface cards (NICs), facilitating seamless expansion as network requirements evolve.
- Efficient Data Transmission: Data transmission in a bus topology is straightforward, with information traveling along the bus from one device to another. This direct communication pathway minimizes latency and overhead, resulting in efficient data transfer rates and low transmission delays.
Applications of Bus Topology:
- Local Area Networks (LANs): Bus topologies are commonly used in LAN environments, particularly in small office or home networks where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are paramount. They provide a straightforward and reliable means of connecting devices within a confined area, such as a single building or floor.
- Educational Institutions: Bus networks find applications in educational institutions, where they serve as a practical tool for teaching networking concepts and principles. Simple to set up and understand, bus topologies offer an ideal platform for hands-on learning and experimentation.
- Industrial Automation: In industrial settings where robust and reliable communication is essential, bus networks are deployed to connect sensors, actuators, and control systems. Their simplicity and efficiency make them well-suited for real-time monitoring and control applications.
The bus network topology offers a compelling combination of simplicity, efficiency, and scalability, making it a versatile choice for various networking environments. Whether in local area networks, educational institutions, or industrial automation, the inherent advantages of bus topologies contribute to reliable and cost-effective network connectivity. By understanding its principles and applications, network administrators can leverage the strengths of bus networks to build efficient and resilient communication infrastructures.