In the realm of networking, where efficiency and reliability are paramount, choosing the right topology can make all the difference. Among the various options available, the ring network topology stands out for its unique structure and practical applications.
What is a Ring Network Topology?
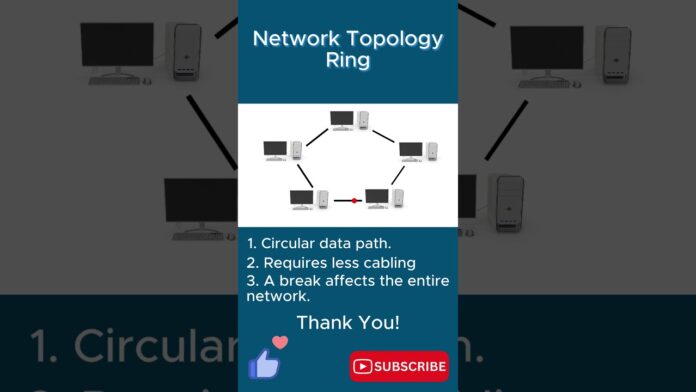
A ring network topology is a configuration where network devices are connected in a circular manner, forming a closed loop. Each device is linked to exactly two others, creating a continuous pathway for data transmission. Unlike other topologies, such as bus or star, where data flows in a linear or centralized manner, a ring topology facilitates bidirectional data transfer within the loop.
Advantages of Ring Topology:
- Resilience: One of the key advantages of the ring topology is its resilience. In the event of a link failure, data can still reach its destination by traveling in the opposite direction around the loop. This redundancy ensures continuous operation even under adverse conditions.
- Efficient Data Transmission: Data travels along a predefined path, minimizing collisions and optimizing transmission efficiency. This streamlined flow of information results in faster data transfer rates compared to other topologies.
- Scalability: Ring networks can easily accommodate additional devices without disrupting the existing infrastructure. New devices can be seamlessly integrated into the loop, making scalability a straightforward process.
- Uniform Performance: Since each device has an equal opportunity to transmit data, ring topologies offer uniform performance across the network. This balanced distribution of traffic prevents congestion and ensures consistent network speeds.
Applications of Ring Topology:
- Local Area Networks (LANs): Ring topologies are commonly used in LAN environments, especially in small to medium-sized networks where reliability and efficiency are priorities. They provide a cost-effective solution for connecting devices within a confined area, such as offices or academic institutions.
- Industrial Automation: In industrial settings where robust and resilient communication networks are essential, ring topologies find widespread use. They support real-time data exchange between sensors, controllers, and other equipment, enabling seamless automation and control processes.
- Telecommunications: Ring networks play a crucial role in telecommunications infrastructure, particularly in fiber-optic networks. The inherent redundancy of ring topologies ensures continuous connectivity, making them ideal for mission-critical applications such as voice and data transmission.
The ring network topology offers a compelling blend of resilience, efficiency, and scalability, making it a valuable choice for various networking scenarios. Whether in local area networks, industrial automation, or telecommunications, the inherent advantages of ring topologies contribute to reliable and robust connectivity. By understanding its principles and applications, network administrators can leverage the strengths of ring networks to build efficient and resilient communication infrastructures.